All in One Moringa Healing Supplements for you
“Oil” “Leaves” “Roots” “Flowers” “Bark” “Seeds”
Moringa oleifera, also known as horseradish tree, ben tree, or drumstick tree, is a small tree from India, Pakistan, across Africa and Nepal that has been used for generations, has been praised for its health benefits for thousands of years in African and Eastern countries to treat and prevent diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, anemia, arthritis, liver disease, and respiratory, skin, and digestive disorders. It is very rich in healthy antioxidants and bioactive plant compounds. So far, scientists have only investigated a fraction of the many reputed health benefits.

Moringa has become popular as a natural leaf powder supplement, although the pods, roots, bark, flowers, seeds, and fruits are also edible.
Almost all parts of the tree are eaten or used as ingredients in traditional herbal medicines. This especially applies to the leaves and pods, which are commonly eaten in parts of India and Africa.

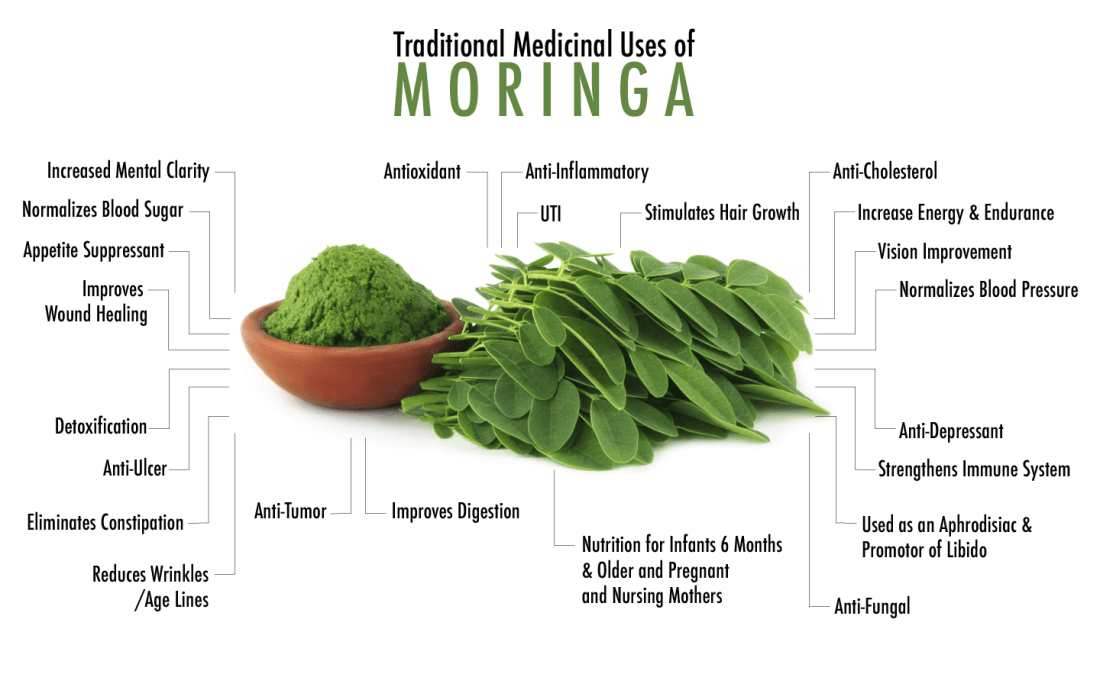
It’s used as a traditional remedy for many ailments
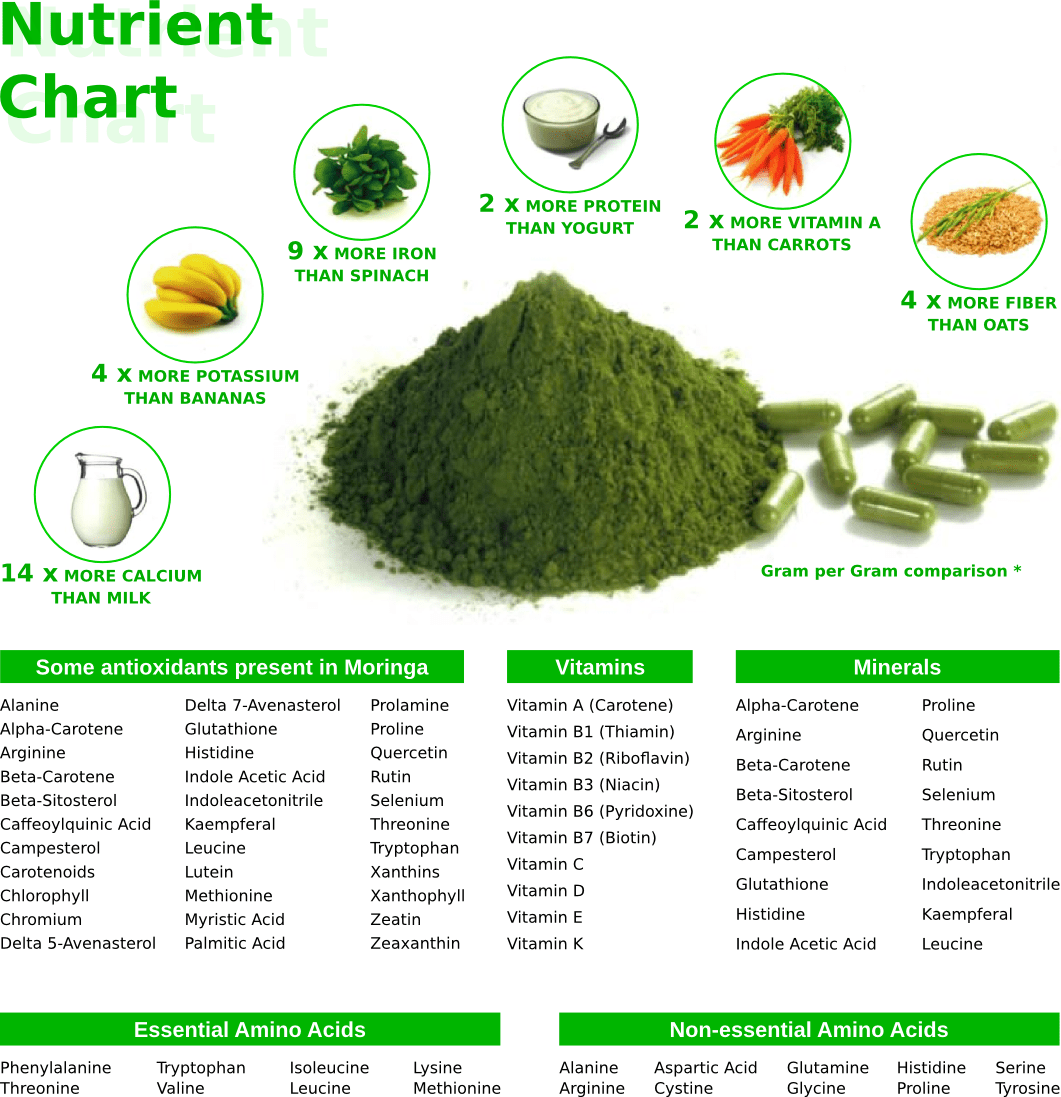
Moringa leaves are an excellent source of many vitamins and minerals. One cup of fresh, chopped leaves (21 grams) contains (2):
- Protein: 2 grams
- Vitamin B6: 19% of the RDA
- Vitamin C: 12% of the RDA
- Iron: 11% of the RDA
- Riboflavin (B2): 11% of the RDA
- Vitamin A (from beta-carotene): 9% of the RDA
- Magnesium: 8% of the RDA
In Western countries, the dried leaves are sold as dietary supplements, either in powder or capsule form.

Compared to the leaves, the pods are generally lower in vitamins and minerals. However, they are exceptionally rich in vitamin C. One cup of fresh, sliced pods (100 grams) contains 157% of your daily requirement.
The diet of people in developing nations sometimes lacks vitamins, minerals and protein. In these countries, Moringa oleifera can be an important source of many essential nutrients.
However, there is one downside: Moringa leaves may also contain high levels of antinutrients, which can reduce the absorption of minerals and protein (3, 4).
Another thing to keep in mind is that taking Moringa oleifera supplements in capsules won’t supply a large number of nutrients.
The amounts are negligible compared to what you consume if you eat a balanced diet based on whole foods.
SUMMARY
Moringa leaves are rich in many important nutrients, including protein, vitamin B6, vitamin C, riboflavin and iron.
Moringa Oleifera Is Rich in Antioxidants
Antioxidants are compounds that act against free radicals in your body.
High levels of free radicals may cause oxidative stress, which is associated with chronic diseases like heart disease and type 2 diabetes (5, 6).
Several antioxidant plant compounds have been found in the leaves of Moringa oleifera (7, 8, 9).
In addition to vitamin C and beta-carotene, these include (10, 11):
- Quercetin: This powerful antioxidant may help lower blood pressure (12, 13).
- Chlorogenic acid: Also found in high amounts in coffee, chlorogenic acid may help moderate blood sugar levels after meals (14, 15).
One study in women found that taking 1.5 teaspoons (7 grams) of moringa leaf powder every day for three months significantly increased blood antioxidant levels (16).
Moringa leaf extract may also be used as a food preservative. It increases the shelf life of meat by reducing oxidation (17).

SUMMARY
Moringa oleifera is rich in various antioxidants, including quercetin and chlorogenic acid. Moringa leaf powder can increase blood antioxidant levels.
Moringa May Lower Blood Sugar Levels
High blood sugar can be a serious health problem. In fact, it’s the main characteristic of diabetes.
Over time, high blood sugar levels raise the risk of many serious health problems, including heart disease. For this reason, it’s important to keep your blood sugar within healthy limits.
Interestingly, several studies have shown that Moringa oleifera may help lower blood sugar levels.
However, most of the evidence is based on animal studies. Only a few human-based studies exist, and they’re generally of low quality (18, 19, 20).
One study in 30 women showed that taking 1.5 teaspoons (7 grams) of moringa leaf powder every day for three months reduced fasting blood sugar levels by 13.5%, on average (16).
Another small study in six people with diabetes found that adding 50 grams of moringa leaves to a meal reduced the rise in blood sugar by 21% (21).
Scientists believe these effects are caused by plant compounds such as isothiocyanates (22).
SUMMARY
Moringa leaves may lead to reduced blood sugar levels, but more research is needed before any solid recommendations can be made.
Moringa Oleifera May Reduce Inflammation
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to infection or injury.
It’s an essential protective mechanism but may become a major health issue if it continues over a long period of time.
In fact, sustained inflammation is linked to many chronic health problems, including heart disease and cancer (23, 24).
Most whole fruits, vegetables, herbs and spices have anti-inflammatory properties. However, the degree to which they can help depends on the types and amounts of anti-inflammatory compounds they contain.
Scientists believe that isothiocyanates are the main anti-inflammatory compounds in moringa leaves, pods and seeds (25, 26, 27).
But so far, research has been limited to test-tube and animal studies. It remains to be seen if Moringa oleifera has similar anti-inflammatory effects in humans.
SUMMARY
In animal and test-tube studies, Moringa oleifera has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties.
Moringa Can Lower Cholesterol
Having high cholesterol has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
Fortunately, many plant foods can effectively reduce cholesterol. These include flaxseeds, oats and almonds.
Both animal- and human-based studies have shown that Moringa oleifera may have similar cholesterol-lowering effects (7, 18, 28, 29).
SUMMARY
Moringa oleifera can lower your cholesterol levels, potentially reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Moringa Oleifera May Protect Against Arsenic Toxicity
Arsenic contamination of food and water is a problem in many parts of the world. Certain types of rice may contain particularly high levels (30).
Long-term exposure to high levels of arsenic may lead to health problems over time.
For instance, studies have linked long-term exposure to an increased risk of cancer and heart disease (31, 32).
Interestingly, several studies in mice and rats have shown that the leaves and seeds of Moringa oleifera may protect against some of the effects of arsenic toxicity (33, 34, 35).
These results are promising, but it’s not yet known whether this also applies to humans.
SUMMARY
Animal studies suggest that Moringa oleifera may protect against arsenic toxicity. However, this has not yet been studied in humans.
The Bottom Line
Moringa oleifera is an Indian tree that has been used in traditional medicine for thousands of years.
However, only a few of its many reputed health benefits have been studied scientifically (1).
To date, studies show that Moringa oleifera may lead to modest reductions in blood sugar and cholesterol. It may also have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects and protect against arsenic toxicity.
Moringa leaves are also highly nutritious and should be beneficial for people who are lacking in essential nutrients.
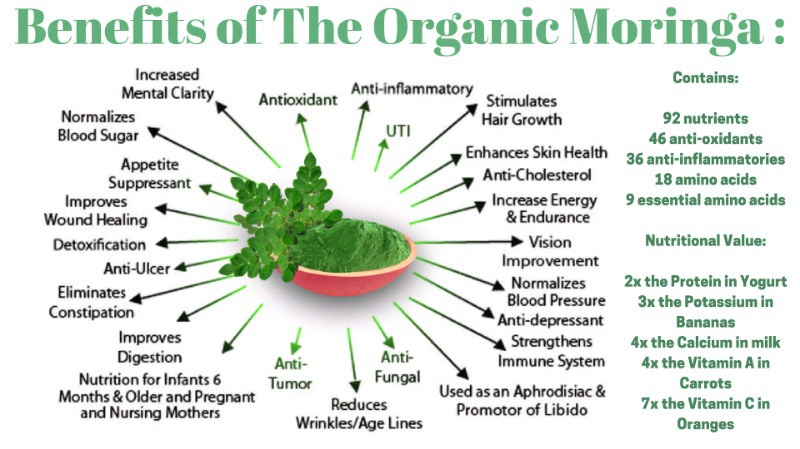
Moringa plant is beginning to gain more popularity as a new “superfood” for its highly nutritious profile and powerful anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and tissue-protective properties among many other health benefits.
Moringa oleifera, also known as horseradish tree, ben tree, or drumstick tree, is a small tree from India, Pakistan, and Nepal that has been used for generations in Eastern countries to treat and prevent diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, anemia, arthritis, liver disease, and respiratory, skin, and digestive disorders.
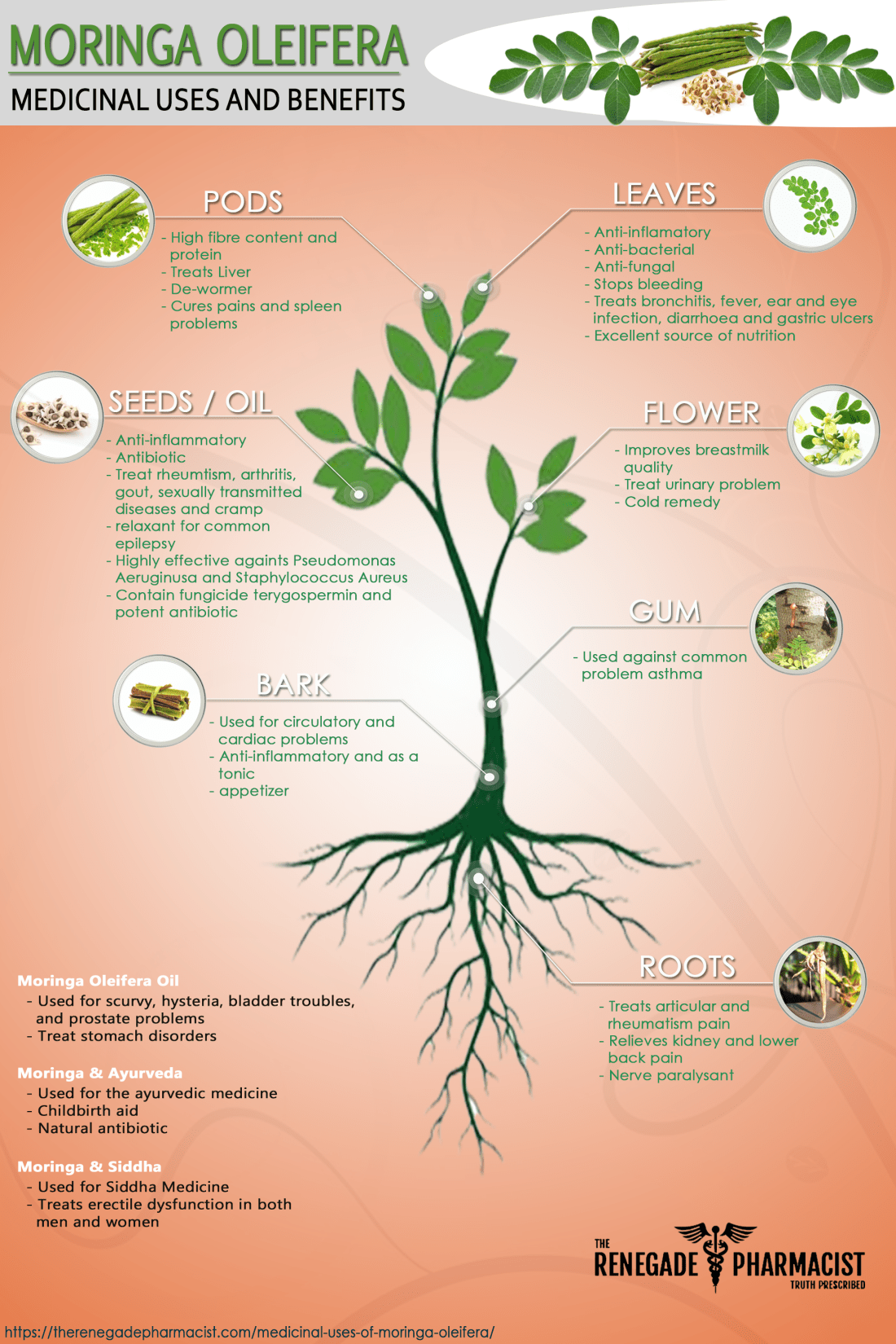
Moringa has become popular as a natural leaf powder supplement, although the pods, roots, bark, flowers, seeds, and fruits are also edible.
It’s used as a traditional remedy for many ailments, and here are 10 scientifically backed health benefits of consuming the moringa leaf:
- It’s nutrient-packed.
Moringa is a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and amino acids. It contains significant amounts of vitamin A, C, and E; calcium; potassium; and protein.
- It fights free radicals.Antioxidants fight free radicals, molecules that cause oxidative stress, cell damage, and inflammation.Moringa contains antioxidants called flavonoids, polyphenols, and ascorbic acid in the leaves, flowers, and seeds.A study found that leaf extracts had higher antioxidant activity, free-radical-scavenging capacity, and higher inhibition of lipid, protein, and DNA oxidation than flowers and seeds.This means it prevents the damage and degradation that free radicals cause in the cells of different organs in the body, keeping them healthy and functioning at their best.
- It fights inflammation.
Inflammation can lead to chronic diseases like diabetes, respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, arthritis, and obesity. Moringa reduces inflammation by suppressing inflammatory enzymes and proteins in the body, and moringa leaf concentrate can significantly lower inflammation in the cells.
- It helps reduce some diabetes symptoms.
Moringa leaf powder has been effective at reducing lipid and glucose levels and regulating oxidative stress in diabetic patients, which means it lowers blood sugar and cholesterol and improves protection against cell damage.
- It protects the cardiovascular system.
Moringa leaf powder has heart-healthy benefits, particularly in blood lipid control, the prevention of plaque formation in the arteries, and reduced cholesterol levels.
- It supports brain health.
Moringa supports brain health and cognitive function because of its antioxidant and neuro-enhancer activities. It’s also been tested as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease with favorable preliminary results.
Its high content of vitamins E and C fight oxidation that leads to neuron degeneration, improving brain function. It’s also able to normalize the neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenaline in the brain, which play a key role in memory, mood, organ function, responses to stimulus such as stress and pleasure, and mental health, for example in depression and psychosis.
- It protects the liver.
Moringa contains high concentrations of polyphenols in its leaves and flowers that protect the liver against oxidation, toxicity, and damage.
Moringa can reduce liver damage and fibrosis and reverse oxidation in the liver. Moringa oil can also restore liver enzymes to normal levels, reducing oxidative stress, and increasing protein content in the liver.
The liver is responsible for blood detoxification, bile production, fructose metabolism, fat metabolism, and nutrient processing, and it can only fulfill these functions with the aid of liver enzymes, so it’s vital they stay at normal levels. For instance, lower levels of hepatic enzymes can impair its ability to filter the blood.
- It contains antimicrobial and antibacterial properties.
Moringa has antibacterial and anti-fungal properties that fight infections. It’s been effective against types of fungi that cause infections on skinand strains of bacteria responsible for blood and urinary tract infections and digestive problems.
- It enhances wound healing.
Moringa has blood-clotting properties in its leaves, roots, and seeds that benefit wound healing and can reduce clotting time, which means it reduces the time it takes for scratches, cuts, or wounds to stop bleeding.
How to Use It
You can add moringa powder to your smoothie or drink it as a tea. The leaf powder was deemed safe in human studies, even in larger doses than normal. The powder has a mild flavor, so it makes for a light moringa tea with a slightly earthy taste.
But you might want to stay clear of seed extract consumption, as they have shown a level of toxicity in immune cells.
Moringa can have laxative effects in large quantities, so a safe dose to introduce it into your food or diet and avoid digestive problems is ½ to 1 teaspoon per day.
by Almoustapha Diakite (diakmusto2@gmail.com)
@Royalsafariphotohouse (Copyright: 2019).
#Niger #Niamey
